What Makes Goji Special?
Keep reading to learn more about this amazing plant.
Why Wellness Seeks Goji
Goji (Lycium Barbarum) has occupied the top tier of nutritional foods for thousands of years and delivers high levels of phytonutrients and antioxidants. Most notably, the Goji fruit and leaf deliver incredibly high levels of naturally-derived Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) when consumed.
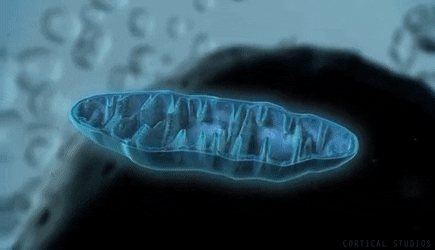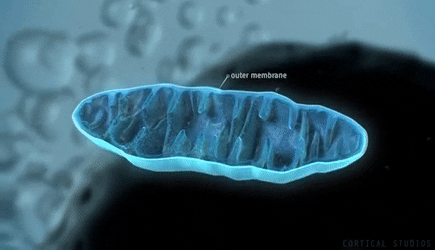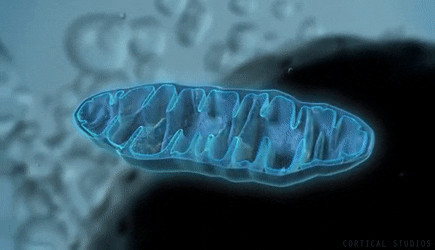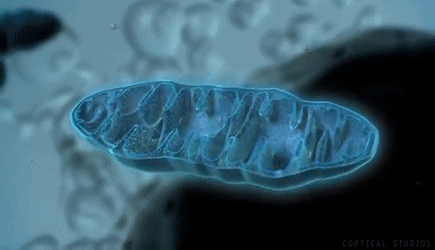
The scientific community has performed extensive research and directly links PQQ as the primary fuel that supports the growth of new mitochondria within the human body. PQQ supports the antioxidants and nutrition within Goji and is an essential natural element to support wellness.
Anti-Aging Discussions Related To Goji
The high levels of PQQ within Goji, along with the body's use of PQQ during cellular regeneration, have led to the continued discussion and study of the plant's "anti-aging" properties. Studies have found that mitochondria use PQQ as fuel, enabling them to function correctly and replicate when needed. Mitochondria are especially abundant in your brain cells and are involved in many critical biological processes, including the regulation of free radicals and neurotransmitters.
“These naturally sweet and delicious little red berries are considered one of the world’s most powerful anti-aging foods. To give you an idea of just how antioxidant-rich goji berries are, they contain three times the antioxidants of pomegranates. They also have a near-perfect balance of essential amino acids, and pack more vitamin C per ounce than oranges. Goji berries are great for your eyes too; they’re loaded with vitamin A which promotes good vision and protects against eye disease.”

The Key To A Healthy Lifestyle
Antioxidants are a crucial part of a healthy diet because they fight free radicals, which are highly reactive metabolites produced by our bodies. They result from our natural biological response to everyday environmental toxins like sunlight, chemicals, and cigarette smoke. The body also produces free radicals when dealing with inflammation and in response to exercise.
Free radicals can affect DNA by disrupting its duplication, interfering with its maintenance, and breaking open or altering its structure. Research has linked free radicals to over 60 different diseases. If the body doesn't receive adequate protection, free radicals can become rampant, causing cells to deteriorate. This leads to tissue degradation and an increased risk of diseases. Here is where antioxidants play an essential role.
via GIPHY
Antioxidants break down the free radical chain reaction. They are the natural way of providing cells with a reliable defense against reactive oxygen species (ROS) attacks. When it has an adequate amount of these essential micronutrients, the body can resist many of the adverse effects caused by everyday exposure to toxins. Without a steady supply of antioxidants to help control free radicals, the body experiences oxidative stress, which can cause tissue and organ damage. But how do we ensure we're getting enough antioxidants?
Fortunately, the human body produces some antioxidants naturally. However, this production is limited and can decline as we age. To maintain an optimal level, we must supplement this natural production by eating antioxidant-rich foods, the best of which are fruits and berries. These include blueberries, blackberries, cranberries, raspberries, and our favorite, Goji berries. Berries also contain potent phytochemicals that prevent certain carcinogens from binding to DNA and are a great source of vitamin C, carotenes, carotenoids, and nutrients like zinc, potassium, iron, calcium, and magnesium.
How Are The Power Of Antioxidants Measured?
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health developed the ORAC Scale to create a standardized unit of measurement for consumers and researchers studying antioxidant levels. The ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) unit, or ORAC Value, measures the antioxidant capacity of different foods and supplements in vitro. The ORAC test provides the free-radical-destroying potential of a given food. It does this by measuring the time an antioxidant takes to react as well as the capacity of antioxidants within the sample food. Foods higher on the ORAC scale will more effectively neutralize free radicals, slow down the oxidative processes, and reduce free radical damage that can contribute to age-related degeneration and disease. The measurement is expressed in terms of a 100-gram sample. It has been suggested that humans should consume about 5,000 ORAC units a day for maximum benefits.
Testing of our beverage, Goji Phyto-Brew, determined that we had achieved an ORAC value of 18,529 per 10 fl. oz. bottle.

Does Life On Earth Have Intergalactic Origins?
In 2004, NASA launched the Stardust mission to chase comet WISE 2 and analyze the contents of it’s dust trails with a mass spectrometer. While reviewing the samples, Dr. Franz R. Krueger discovered evidence of a co-enzyme similar to (PQQ), and stated, "evidence of a co-enzyme similar to Pyrroloquinoline Quinone discovered from the comet is a pre-requisite for life as we know it." Dr. Krueger added:
“I am convinced that it was the arrival of PQQ-laden stardust on Earth 3.6 billion years ago that spawned life on this otherwise lifeless planet.”
Sources and References
What are ORAC Units, ORAC Values: Antioxidant Values of Common Foods.
The 36 Best Ways To Naturally Increase Dopamine Levels In The Brain
Top 5 Highest Antioxidant Foods from Nuts.com (Goji Farm USA is not affiliated with Nuts.com)
Banner images by Cortical Studios and Triff / Shutterstock. Animated gif via GIPHY.

